Recent Advances in Endophthalmitis: A Review
Downloads
Published
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56692/upjo.2023110303Keywords:
Endophthalmitis, Quantitative PCR, Multi-mono PCR.Dimensions Badge
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
© Author, Open Access. This article is licensed under a CC Attribution 4.0 License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/byncsa/4.0/.
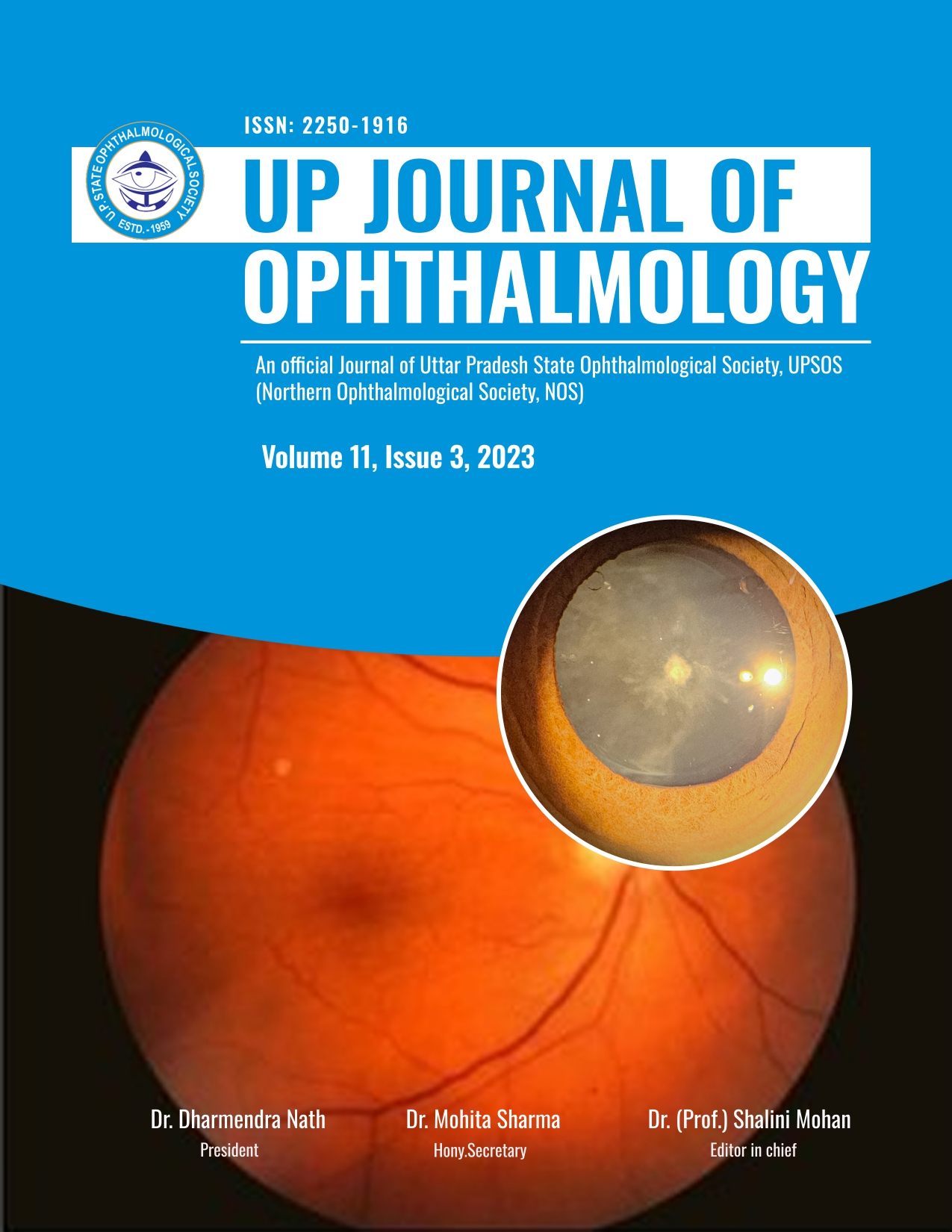
Endophthalmitis refers to inflammation of the inner coats of the eye.it is one of the dreadiest complications for an ophthalmologist. It can present with floaters, ocular pain and redness, and a diminution of vision. Depending on the presence of organisms or toxins, it can be classified into infective and non-infective. Infective endophthalmitis, caused by microbes such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites, can be further subclassified, depending on the entry route, into an exogenous or endogenous approach. Endophthalmitis via exogenous route occurs when the microbes enter the sterile eye environment postoperatively (post cataract or post intravitreal injections) or post-traumatic while endogenous endophthalmitis results from the bloodstream, carrying the infection to the eye. This review aims at highlighting the recent advances in diagnosing, preventing, and treating endophthalmitis. We have gathered our information from various articles published in PubMed. Through this article, we would like to upgrade our scientific knowledge, widen our research field, and pave the way to follow newer trends to combat this grave diagnosisAbstract
How to Cite
Downloads
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Naheed Akhtar, Abdul Waris, Intermittent Exotropia- Management In Current Perspective , UP Journal of Ophthalmology: Vol. 8 No. 03 (2020): UP JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
- Naheed Akhtar, Shairin jahan, Abdul Waris, Nada Nadeem Ansari, S.A.R Rizvi, Vitamin K Bleeding Masquerades as Capillary Hemangioma: Case reprt , UP Journal of Ophthalmology: Vol. 4 No. 01 (2016): UP JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
- Rizvi Sa, Abdul Waris, Naheed ., Oxygen therapy in Preterm :Savior or threat ? , UP Journal of Ophthalmology: Vol. 7 No. 03 (2019): UP JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
- Abdul Waris, Naheed Akhtar, Body Building Protein Supplement Leading to Visual impairment , UP Journal of Ophthalmology: Vol. 4 No. 02 (2016): UP JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
- Raina Garg, Tejal Srivastava, Mohammad Saquib, Abdul Waris, Surgically Induced Focal Scleral Necrosis – A Rare Outcome , UP Journal of Ophthalmology: Vol. 13 No. 02 (2025): UP Journal of Ophthalmology
Similar Articles
- Kshitij Raizada, Mohit Gupta, Dipendra Shukla, Prabhat Ranjan, Endophthalmitis in a Vitrectomised Eye - An Unexpected Visitor , UP Journal of Ophthalmology: Vol. 9 No. 02 (2021): UP JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
- Aditi Jhunjhunwala, Ram Kumar Jaiswal, Pooja Mishra, To Study Ocular Surface Morbidities among Glaucoma Patients on Anti-glaucoma Drops , UP Journal of Ophthalmology: Vol. 10 No. 01 (2022): UP JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
- Deepti Mujumdar, Successful Surgical Outcome in a Case of Monocular Elevation Deficiency after Knapp’s Procedure with Foster Augmentation: A Case Report , UP Journal of Ophthalmology: Vol. 11 No. 03 (2023): UP JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
- Charu Agrawal, Setting Target IOP in Glaucoma , UP Journal of Ophthalmology: Vol. 4 No. 01 (2016): UP JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
- Rajesh Sahay, An Approach to a Patient with Post-Operative Endophthalmitis , UP Journal of Ophthalmology: Vol. 8 No. 02 (2020): UP JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
- Rakesh Porwal, Hemlata Udenia, Imaging Biomarkers in Diabetic Retinopathy , UP Journal of Ophthalmology: Vol. 9 No. 03 (2021): UP JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.